What is SEO?
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimisation, and is the process of optimising your website so that you appear as high as possible in search engine results pages (SERPS) in Google, Bing etc.
There used to be all kinds of techniques to achieve this, and you could pay companies good money to get them to employ the ‘tricks’ for you. The search engines clamped down on the tricks and as a result of these changes, it is now easier to learn how to practice SEO yourself.
Remember that the search engines are businesses, with the searchers as their customers. They want to keep those customers happy, and keep their advertising income high, by returning good, relevant results. Therefore the search engines continuously refine their algorithms.
We all know it is highly beneficial to appear on page 1 of a search engine results page (SERP). SEO is effectively a website’s way of shouting “Pick Me! Pick Me!” to appear first.
Below we concentrate on the search engine Google. Bing is not as popular a search engine, but as many people do use it, it can be useful to not ignore it.
Search Engines
Although we think of search engines as great and free resources, they are in fact businesses.
As mentioned above, searchers are their customers. And as a business they want to keep those customers happy. They do this by returning good, relevant search results.
If searchers continuously get pointless results they will move on to a ‘better’ search engine, i.e. a competitor.

Types of SEO
There are two main types of SEO, namely:
- On page – things done within a website
- Off page – things done off site that can still help with rankings.
Off page includes things such as:
- Being in directories
- Social media campaigns
- Blogging
- Creating quality backlinks for ‘link juice’
- Establishing yourself as an industry expert
- Press releases
- Videos and YouTube
What are algorithms?
Algorithms are a process/set of rules that is followed in determining which webpages to return as results to search enquiries. Furthermore, these refinements are carried out to weed out websites that are still employing the old SEO tricks. They are known as ‘Black Hat SEO’.
Google uses over 200 ranking factors in its algorithms.
Some are widely known, many are only known to those who take an interest in the subject and many are still a mystery to anyone but Google itself.
Google has created a useful article if you want to really understand How Search Algorithms Work.
What are SERPS?
The search results pages (SERPS) are the pages you want your organisation to be at the top of, or at least as near to the top of as possible.
SERPS are what we see when we do a search. Every SERP is unique, because Google customises the results based on a wide range of factors beyond the search term. Such as your:
- physical location
- browsing history
- social settings
Although GDPR may have had some impact on this.
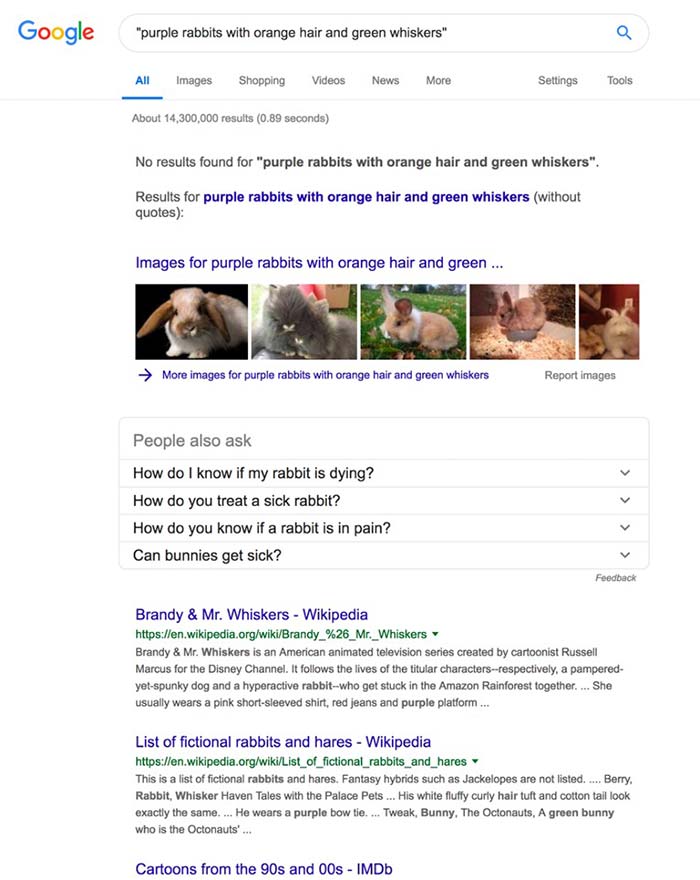
“Page 1 of Google” is a myth that some people will try to sell you.
It is possible to guarantee a page 1 Google SERP. In the example here we could have a site ranking number 1 for
“purple rabbits with orange hair and green whiskers” within days.
What is not possible, is to guarantee that a site will actually be found and then receive traffic from a SERP.
Remember that, if no one is searching for what a site is offering, it will never be returned as a search result.
What is down ranking?
As well as deciding which pages to return in the SERPS, the algorithms also look for factors that will get your website not ranked.
Simply put if your site ‘breaks the rules’ it will not only not be returned as a search result, the site itself will be down ranked.
This could mean your whole site is no longer listed on SERPS. Or, certain key phrases that you had ranked well for are now no longer ranking at all. If the site is no longer returned in the SERPS, your target audience will not be able to find you.
Although there are many more factors that a search engine might consider, these are the most common:
- The site has evidence of spyware, adware, or viruses
- Links are deliberately hidden in text
- Unexpected URL redirects that take a site visitor to another page without them clicking to do so
- Content filled with non-relevant keywords
- Overuse within text of a genuine key phrase
- Using duplicate content, which means using material copied from another source, or using the same content of your own multiple times within your site
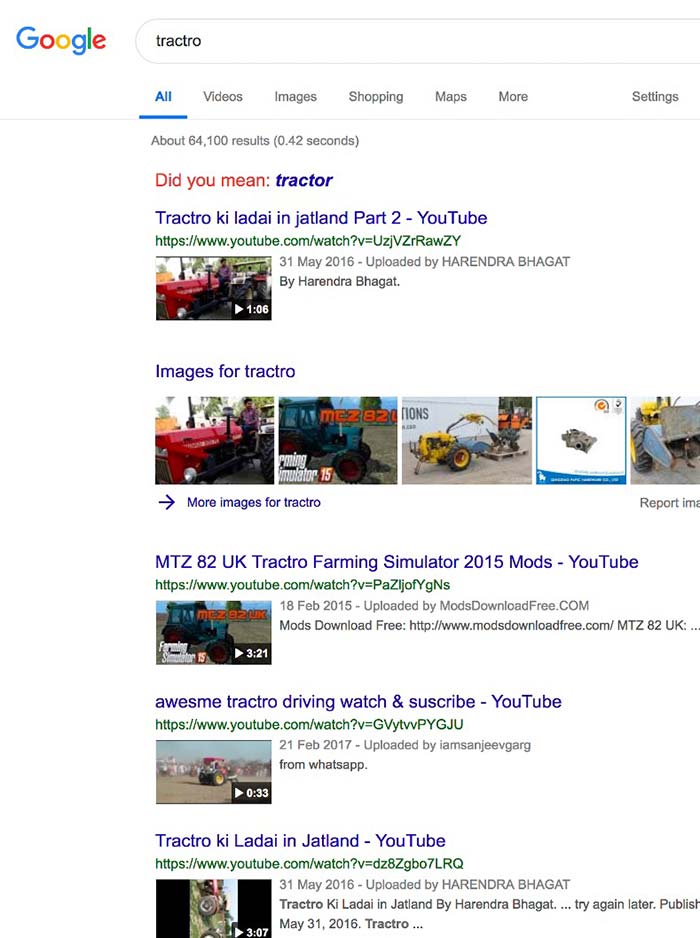
Is Google really all knowing?
As searchers it is easy to think that Google understands everything. Take a simply typo of ‘tractro’ for example. Google asks you if you mean ‘tractor’.
But, SEO is not about being a searcher; it is about telling Google, with extreme precision, what a website is about.
- The searcher wants a perfect solution
- Google finds 1,000s of sites to chose from to create a SERP
- The more it understands what a site is about, the easier it is for it to decide whether to rank it or not
- Google wants to return great results for its customers
- The more we tell Google, the easier it is for it to understand the site
- When Google understands the site versus the search query, the more they match, the higher the site ranks
How to accomplish SEO
It is now potentially simpler than it has ever been. To get found on a search engine all we have to do, in very simple terms, is make sure that our website offers, what the search engine totally believes, a searcher is actually looking for.
Imagine you head to Google and search for a red hat to buy. Would you want to see a website that was last updated in 2010? You probably don’t want to see a website that says “buy red hats here”, and then turns out to be a load of links to other, unrelated, websites?
What you want to see is sites that offer various red hats for sale. Websites that look up to date, trustworthy and safe to buy from.
So how do the search engines try to find these ‘good’ sites? The algorithms look for various indicators such as:
- that the site is current
- it is very relevant to the search term
- it has a decent reputation
- it offers the product or information the searcher is looking for
- it also contains unique content
- in the case of Google, they check if you are using their other products
How do we add these indicators to our site?
- Current – keep fresh content e.g. blog posts, new products or any other updated content, e-newsletters.
- Relevant – content that the searcher finds informative, engaging, helpful, or entertaining. Also pay attention to your location; if you are a Nottingham plumber make sure you reference Nottingham.
- Public reputation – reviews, blog comments, activity on Social Media, your Social Media posts on your site etc.
- Internet reputation – relevant links to your site from high quality websites such as Local Government, the BBC, Huffington Post etc.
- Information – use relevant keywords; make sure a page about blue widgets contains the phrase ‘blue widgets’ in the pages title, in the page text, the meta tag description and in the image name of any pictures on the page. However, do not go overboard and put ‘blue widgets’ in every sentence. The text must read well.
- Unique content – just as it says, make your content unique. Do not copy anyone else’s content; do not use product descriptions given to you by suppliers. Rewrite them to suit your business.
- Google products – use YouTube, have Google analytics on your website, claim your business on Google My Business etc.
The ‘magic’ formula
If searchers are using search terms that are not on a site, or at least not enough to convince Google that it should appear in a SERP, the site will not rank.
What is needed is:
A site optimised for the business’ keywords (key phrases)
+ using specific keyphrases that searchers actually use
+ using those keyphrases that searchers actually use
BUT your competitors do not use
= high Google rankings on potential customers’ SERPS
What SEO techniques can I implement myself?
Follow the tips above and also make sure that, once you have established your Focus Keyphrase(s) per page/post/category/product, that it appears in:
- Page name & title
- URL slug
- Content
- Meta title
- Meta description
- Image title
- Image Alt text
- Product short description or excerpt
To help with this we recommend you follow all the on page instructions that ‘RankMath’ provides. Although the SEO analysis below is classed as ‘ok’, you can see that Yoast is still suggesting improvements that can be made. In the case of this product, if there were 300 words in the content Yoast would class it as ‘good’.
We are in the process of migrating our client sites to RankMath and will add further instructions as soon as we can.

Your industry can help
Factors that make SEO easier in a particular industry:
- Being in a niche market
- Selling very specific products
- Having a low number of competitors
- Having competitors not using SEO
- Catering to a local market or area
- How customers interact with your business
Do not use iFrames
Quite simply, Google cannot understand them.
If you do use iFrames then try to to find a product, that exists, on Google. Even using a very specific search term, nothing will be found.
What is Schema Markup?
Schema Markup or ‘rich snippets’ is a form of microdata that, once added to a webpage, creates an enhanced description. Thus making it easier for Google to know what the page is about.
There are a set of schemas already defined:
- Businesses and organisations
- Events
- People
- Products
- Recipes
- Reviews
- Videos
- How to articles
- FAQs
- And many more
Schema markup can be painstakingly added manually. Or we can do it for you dependent on which of our SEO packages you take.
Notice the extra information on the recipe links with schema markup.
What are SEO specialists getting paid for now?
It is all very well knowing you need to add fresh content all the time and sprinkling your keywords about and ‘engaging’ on Social Media, but we often do not have the time for this.
In addition, what if we are saying the wrong things? It is no good posting to Twitter “we sell red hats” every five minutes. That is of little interest and gives no value to the reader.
Most of all you need to share things that people will want to read because they do not think they are being sold to. “Do you know why red hats are sexy?” will get attention, and is more likely to result in sales.
Special offers and discounts are different though. “50% off red hats today only” is of interest. And what if no one is even listening anyway? It can be a bit of a catch-22; by spending the time on this content we will be more successful. Yet we cannot afford to spend this time until we are more successful…. The solution may be to buy in this kind of SEO expertise:
- Have regular blog posts written for you.
- Add your Schema Markup
- Get genuine followers and likers found for you (do not buy followers etc!)
- Show Social Media feeds on your website
- Have your Social Media campaigns run for you.
- Have keyword research carried out for you; there is no point using a keyword that no one is searching for in the first place.
- Have your Google Analytics and Search Console accounts managed for you.
- Have your Bing Analytics and Webmaster Tools accounts managed for you.
- Get professional help generating quality backlinks
If you decide to go down this route, make sure you have a budget for this work and monitor whether it is successful or not.
Lots of traffic to your site might be great, but if the visitors are not doing what you need them to: buy something, call you etc. then they are not worthwhile.
We offer several professional SEO packages that you may be interested in.
